Logistics is increasingly important for the economy. Concerning this statement, we can say that logistics, in a developed industrial country, accounts for about 12% of GDP. Given that logistics have a broad sense, we talk about supply chain, and in this area we find not only transport companies and logistics operators, but also storage companies, manipulations, hardware and software specialized in the sector, consultancies, etc.. Figures that are not surprising if we take into account the growing importance of logistics both in industrial processes and in distribution of products, due to the unstoppable increase of e-commerce.

In this context, it is essential to increase logistics efficiency if we want a viable future for the country, because of the weight that it already has in the economy and for the importance it has in making industrial production viable.
It must be said, however, that the increase in efficiency cannot be done easily, we have a double challenge: increase efficiency and at the same time preserve the environment, in both, we have no choice. Surely we can have plan B for many things, but there is no plan B for the planet, it is necessary to stop climate change as it is.
The Paris Agreement of December 2015 that will begin to be applied in a serious way in 2020, with already measurable objectives in 2021, forces to a very important reduction of gas emissions and greenhouse effect. The objective is that by 2050 the reduction will be drastic and almost total in sectors such as the transport of people and goods.
In which direction does the logistics sector advance?
Despite having very important targets for greenhouse gas reductions, the trend in the sector is clearly increasing for a number of reasons, but the main ones are:
Reasons
- An important growth enhanced by processes of relocation of production.
- The internationalization of business relations.
- The development of e-commerce.
Consequences
We must bear in mind that this remarkable growth has consequences amongst those that stand out:
More emissions and pollution
A very important volume of global greenhouse gas emissions are due to logistics activity.
More infrastructure
Infrastructures needed for economy growth, also cause a great environmental impact.
More waste
We increasingly use more packaging, we carry out an ineffective and unsustainable management of them.
Main challenges of the logistics sector
As we have seen, the challenges of the sector are enormous. We must act on many fronts if we want to achieve them. Below we will detail some of the strategies that have been initiated.
More efficient vehicles
In this context, the commitment to vehicles that allow maintaining an effective operation is fundamental, reducing their environmental impact, such as hybrid, electric, natural gas vehicles, etc.
Compliance with the CAFE Law
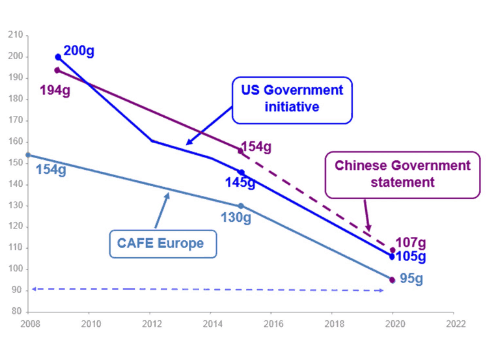
It is a United States, Europe, China and other countries law that forces the average emissions of new brand car lines, to reduce their polluting effect, following the reduction targets that are seen to graph 1.
How to achieve it:
- Reducing the exterior volume of vehicles, but keeping the interior volume for the occupants.
- Improving aerodynamics, it must be said that projected area reductions of about 5 square meters have an impact of reductions of 2 grams of CO2.
- Optimization of the market mix of the brand. As the value is measured on the average of the whole brand, the smaller vehicles are, hybrid or electric vehicles with lower emissions can be compensated for those with higher emissions.
- Betting on new propulsion systems. Optimizing the propulsion system. Improving the emission of the motors. Using hybrid systems (complement traditional gasoline or diesel engine with electric propulsion system). Using 100% electric vehicles.
- Minimizing the bearing resistance.
- Reducing the weight of the vehicle (the less weight the vehicle has, the better, since smaller engines can be used and with lower emissions).
- Using lighter materials in the manufacture of vehicles. Aluminum as a substitute for steels. Materials composites (alternative that is considered with greater possibility of reduction of weight, but currently with more direct costs).
3D additive printing
The 3D additive printing on demand allows personalization and immediacy, basic features of the new industry 4.0. As 3D printing technology manages to reduce unit cost and increase print speeds, more and more things are produced, not just prototypes.
This type of production will drastically change the logistics needs, will make the logistics operators also become industrial, making products in their facilities close to consumers. This phenomenon will reduce the length of the logistics chains, also reducing its polluting effects.
Intelligent logistics operation
Improvements in efficiency and effectiveness of operations
- Modularization of packaging systems
- Real-time decisions: Synchromodality. Slow steaming
- Trucks without driver
- Aggregation of online demand
- Scheduling part of the activity at less busy hours
Sustainable infrastructures
That allow to improve and increase the competitiveness, for example:
- Sustainable roads, capable of self-supply and being profitable
- More sustainable warehouses (waste, energy, etc.)
- Intervention on territorial policies (last mille regulation, access cities, demand aggregation (urban and / or regional platforms), etc.).
- Guarantee the multimodality is key (increase rate utilization).
- Green freight brokers (EU initiative)
Role of logistics in circular economy
In this regard, it is worth mentioning the essential role that logistics must play in the circular economy model, in particular:
- Reverse logistics.
- The role of the logistics sector as a “resource / waste manager”.
- The design of environmentally respectful containers and packaging.
- Models that allow the reuse of the packaging
To achieve this, collaboration is the key.
New business models
In addition, new business models are emerging to take into account the strategy posed. A good example of this is:
- Collaborative consumption, new generations are increasingly seeking the experience and not the possession of products.
- Distributed logistics, so-called Internet physics. This concept will drastically change the way we do things.
- E-commerce, needs immediacy, we are already seeing efficient alternatives for the last mile, such as:
- The use of intelligent ticket offices.
- The convenience points.
- The optimization of routes.
- Drones (once the legislative barriers are over)
- Collaborative distribution
- Micro-platforms
If the question is whether Logistics 4.0 will be sustainable, the answer is that it has no option, it must be. To achieve this, the challenge is enormous and requires organizations innovation, flexibility and adaptability. If we face the changes without fear but with responsibility and betting on innovation and transparency, I have no doubt that we will achieve this.


