Currently, the data revolution and its management are the subjects of new developments and solutions, those that allow efficiency and response speed to the needs of business systems and processes.

Companies are in transition towards digitization, which leads to the application of technologies such as IoT, Big Data, 5G, among many others. For this reason, these technologies must be able to support and dynamize the tasks practically immediately to be an investment that enhances the possibilities of transformation towards the future of the market.
What is Fog Computing?
Fog Computing is a technological process that seeks to streamline data management and storage. It is a distributed architecture where smart devices are at the edge of the network, to locate basic analytical services much closer where they are needed. This allows a tome reduction to transmit data, improving the performance and efficiency of the overall network. This development goes hand in hand with Edge and Cloud Computing, towards the development of an intelligent dynamism for information management.
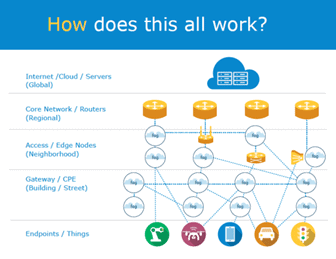
Fog allows services to be distributed closer to things and anywhere on the continuum between the cloud and things (endpoints). Source: https://blogs.cisco.com/innovation/new-reference-architecture-is-a-leap-forward-for-fog-computing
Advantages of fog computing
Improve security and privacy control:
Its paradigm is based on segmenting traffic, which allows solving many security problems, thanks to additional firewalls in the network. Also, the alternative of processing confidential data locally, instead of in the cloud, makes it possible to prevent the breach of confidential data. Fog computing has the advantage of being able to act as a proxy for devices with limited resources, to update software or security credentials.
Greater market agility:
The fog allows knowing in advance what resources customers need, where and when they need them, allowing a rapid response to consumer demands, which is a competitive advantage for companies.
Fog networks allow users to offer more specific services and solutions, as well as place data and data tools where they are best processed, all based on existing computing infrastructure and capacity.
Improve reliability and minimize latency:
Its intelligent process is reliable as it is possible to reduce the data transmission load and automatically optimize its optimal performance. Cloud computing can function independently and ensure uninterrupted services even with fluctuating network connectivity to the cloud.
Fog performs all urgent actions close to end-users, alleviating device and application latency limitations. On the other hand, thanks to the speed to perform data analysis in real-time, it is possible to have faster updates, reduce security dangers for users and improve workflows.
Reduce operating costs and conserve bandwidth:
By processing selected data locally, Fog Computing can save network resources as it is an alternative to analyze it close to the source, instead of automatically uploading it for analysis in the cloud.
Fog computing chooses the data to process based on application demand, available networks, and computing resources. This reduces the amount of data to transfer to the cloud, ultimately saving network bandwidth.
Fog computing, Edge Computing and Cloud computing. What is the difference?
Edge Computing is a subset or component of Fog Computing. To explain this with an analogy: Imagine fog computing is a box of toys, Edge Computing would be just one variety of toys. Edge computing refers to the data that is analysed at the point of creation. Instead, the fog encapsulates all processing at the edge, as well as the network connections necessary to get the data from that edge to its endpoint.
Therefore, Edge and Fog Computing are complementary. Therefore Cloud Computing is responsible for storing and processing data in data centres located in remote locations. This remoteness is key for differentiating Fog from Cloud. The best way to understand it is by using its literal meanings. Fog are clouds closer to the ground, so is a layer that is placed to reduce latency in some scenarios. This forms a close integral platform with the power to process important data and analyze it, generating a fast alternative that supplies computing power when the same devices or the amount of data cannot do it or they are urgent.
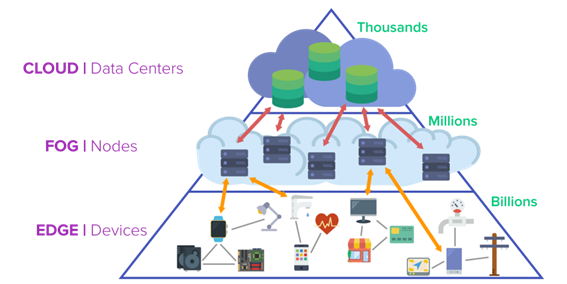
Source: https://www.omnisci.com/technical-glossary/fog-computing
Fog computing can solve IoT challenges
The IoT scenario is one of the best for the application of fog computing. IoT applications generate a large amount of data that requires processing and sometimes it is not possible or necessary to send it to the cloud. Fog can be the best alternative to provide control, speed, and analysis.
These advantages are useful for developments looking for a fail-safe and systemic technology application, such as Smart Cities, security, Smart Buildings, transportation, etc. Let’s see some examples:
Smart Home
A Smart Home consists of several connected devices and sensors. These devices have different platforms, which often makes their integration difficult. Fog computing can provide a unified interface to integrate all these independent devices and provide flexible resources for storage, real-time processing, and low latency.
Telemedicine
Cloud computing enables real-time information processing to respond to events that are critical to quality healthcare. Additionally, it can also address issues related to network connectivity and traffic required for remote storage, processing, and retrieval of medical records from the cloud.
https://www.ekon.es/telemedicina-hacia-la-diagnosis-remota/
Smart Cities
There is a huge variety of problems that big cities face, including public safety, sanitation, high electricity consumption and services of all kinds. To support the integration of this entire complex ecosystem, the objective is to design a network deployment of fog nodes for cities, so that there is a single, smarter IoT network without saturations.
In short, Fog Computing is a relevant alternative given the rise of the IoT worldwide. It provides the solution to speed and data explosion problems. With the advantages of saving bandwidth, improving latency and the possibility of obtaining faster and deeper knowledge in less time and with greater security.
It is an infrastructure with the power to meet all the requirements so that technologies focused on data management can enhance their development.
This development is key for large and small scale digitization, it is an alternative that will support the Data Revolution, become a reality and that we can enjoy fluid and reliable digital systems.


