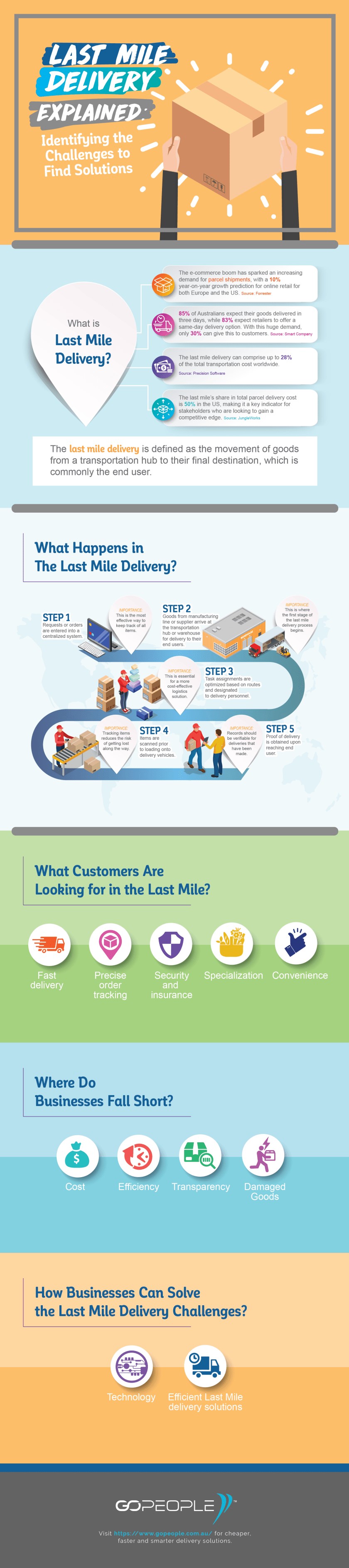
Last mile delivery, is defined as the last movement of goods from a transport center to the final delivery destination. The main last mile logistics objective is that the delivery of the items is as fast and efficient as possible.

Quality in the last mile delivery is a key differentiator, if the consumer can easily buy and the product is delivered in conditions and quickly, companies gain market share and loyalty from the customer.
We know that more and more consumers are turning to e-commerce to make their purchases. The “fast” delivery requirement is no longer just a luxury but also an expectation that they look for in each online shopping experience. Given this, companies and startups are developing new technologies and experimental models to increase the volume of packages, expedite deliveries and delight customers, all while trying to reduce costs.
Last mile delivery logistics problems.
The most common problems faced by companies involved in this type of logistics, broadly speaking, could be broken down as follows:
- Poor infrastructure: Especially in developing countries, this means longer trips, inefficient routes and transport. All this translates into increased costs and delays.
- B2C and C2C deliveries: When large volume B2B deliveries are made, additional costs can be cushioned and worthwhile. But, for B2C or C2C deliveries the extra costs fall on a single package of variable cost and often reduced price.
- Special goods: On some occasions, even the type of goods can contribute to be a challenge for delivery. For example: Toxic, fragile, perishable or flammable items, which require more planning.
- Customer Derivatives: This may be the biggest challenge. Phenomena such as incorrect addresses, remote locations, narrow streets, client absence to receive the package, capricious cancellations, returned orders, etc. This affects the potential costs cannot be calculated accurately.
Instant gratification, the consumer expects everything to be a click away.
The focus of the situation is that the online consumer is increasingly demanding. Doesn’t like to wait. Believes that everything is one click away. This need for “instant gratification” has become the hallmark of the Digital Age and is unlikely to change soon. This consumption on demand will only continue to grow and yesterday’s premium features, such as real-time tracking, deliveries in a few hours and for free, are no longer special and become a standard, the consumer expects no less.
Last Mile Delivery. The need to create assertive strategies.
We have already talked about the problems and challenges to achieve the “instant” satisfaction of a demanding consumer. In order to thrive and not only survive and to take advantage of the online sales boom, which is yet to grow, it is important that companies begin to develop strategies and best practices to ensure that last-mile logistics is profitable, well optimized and successful. Here are some suggestions:
- Real time monitoring:
Consumers are eager to receive their orders, waiting can result in them feeling frustrated, impatient and even distrustful of the service. An intelligent last mile tracking system allows you to see the package current location at all times and provide notifications about your arrival time. This can be effective in relieving stress and uncertainty while waiting.
- Outsource delivery to local companies:
Companies can outsource last mile delivery to local carriers with operations centers near delivery areas. This can help reduce costs and improve delivery speed. Important to note that this external provider will be the face of the company, so it has to be choosen wisely. To manage multiple transport service providers, a good option is to use a Centralized Transportation Management System (TMS) to track deliveries and distribute workload.
- Local commerce as distribution centers:
Local stores have transformed their stores into distribution centers for package delivery. A viable alternative to improve delivery speed and same-day deliveries.
- Data Analysis:
An intelligent tracking system allows companies to have real and accurate data and statistics on delivery strategies. With data analysis it is possible to analyze and improve delivery routes and optimize the strategy. In previous articles I already talked about the need to know your customer, know their preferences, buying habits, etc. If you know this, you can anticipate the orders that are going to be made or even send a package before it has been requested, as Amazon is already starting to do. There is no better logistics than the one that begins before your customer has placed your order.
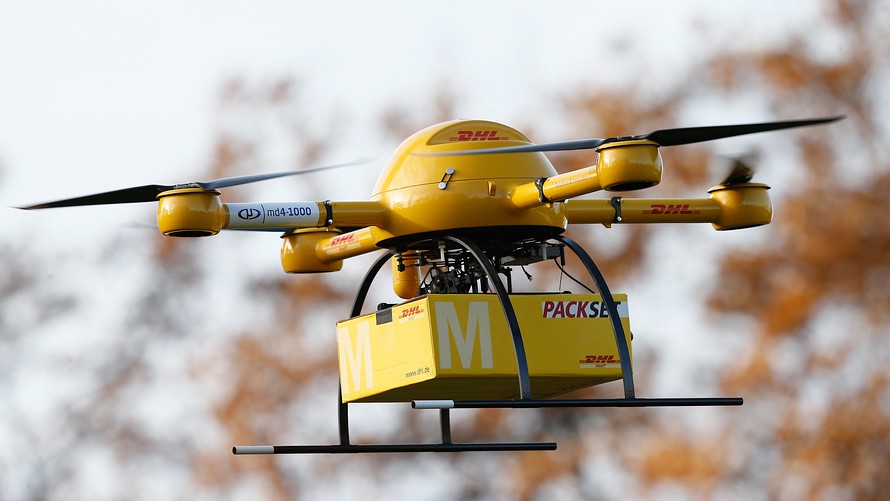
- Automation
With the future around the corner, companies may use autonomous vehicles or drones for the Last Mile Delivery. Amazon Prime is already testing a futuristic Prime Air service through drone delivery, designed to send packages to customers in less than 30 minutes. This type of delivery has many benefits: drones are faster than cars, can save operating costs and reduce the amount of fuel needed. In addition, drones do not require parking spaces.
The automation of each of the Last Mile logistics multiple stages operations can make it easier for companies to reduce processing costs and even increase revenues. Through the integration of those involved in the delivery, the generation of optimized operations and better alternatives for the final consumer, companies can discover new and better ways of doing things; creating an effective, transparent brand image with profitable strategies.
In summary, each of these strategies to create successful and viable solutions for last mile logistics requires the same thing: that companies prioritize efficiency and flexibility. All this range of strategies must be used intelligently, harmoniously, it is about providing the right service to each type of client. We must have the ability to apply them all at once, since none of them solve the problem entirety, but its joint application can lead us to achieve it.